Arthritis & Spine Disorders: Comprehensive Guide to Treatment and Rehabilitation
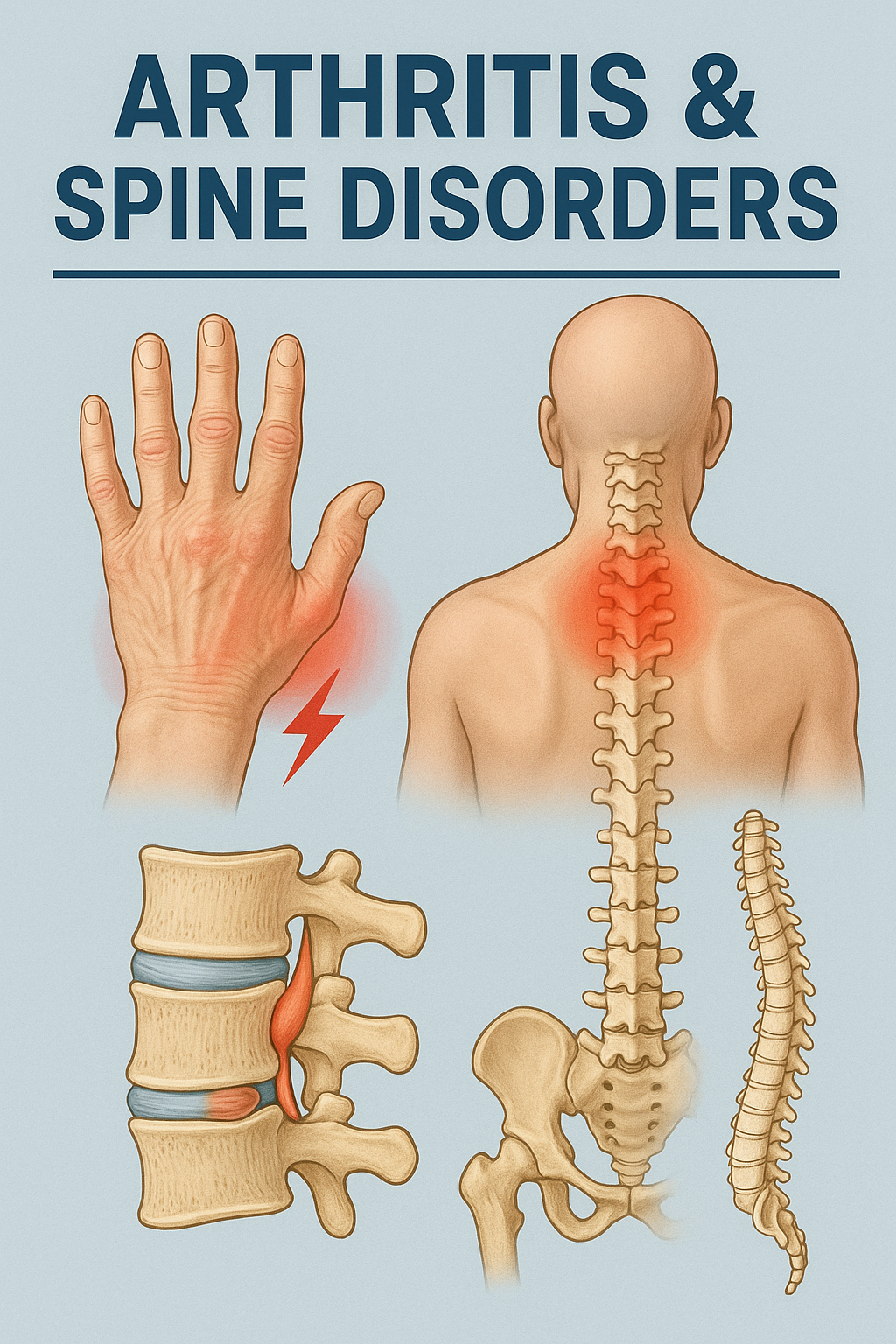
Arthritis is a broad term used to describe a group of conditions that involve inflammation of the joints. This inflammation often leads to pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited movement, making everyday activities like walking, climbing stairs, or even gripping objects difficult.
Contrary to popular belief, arthritis is not just a condition of old age. While it is more common among older adults due to joint wear and tear, it can affect people of all ages, including young adults, teenagers, and even children
Contents ⬇
Arthritis & Spine Disorders | What Are Arthritis | Causes | Symptoms and Diagnosis | Treatment Options | Rehabilitation | Holistic Approaches | Prevention | Conclusion | FAQs
Understanding Arthritis & Spine Disorders
What Are Arthritis and Spine Disorders?
Arthritis refers to inflammation of one or more joints, leading to pain and stiffness. Common types include:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): Caused by wear and tear, it often affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks joint linings.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Occurs in people with psoriasis, leading to joint and skin issues.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Primarily affects the spine, causing stiffness and eventual fusion of vertebrae.
Spine disorders encompass a range of conditions affecting the spinal column, such as:
- Herniated Discs: Displacement of disc material causing nerve compression.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal leading to nerve pressure.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal lateral curvature of the spine.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related disc wear causing pain and reduced flexibility.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Age – Degeneration increases with age
- Family History – Genetic predisposition to arthritis
- Obesity – Adds strain on joints and spine
- Lack of Physical Activity – Weakens support muscles
- Injury or Overuse – Sports injuries, heavy lifting, poor posture
- Autoimmune Disorders – Can trigger inflammation
- Smoking & Poor Diet – Reduces blood flow and joint health
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the Warning Signs
- Joint Pain and Stiffness: Especially after periods of inactivity.
- Swelling and Redness: Indicating inflammation.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving joints or spine.
- Numbness or Tingling: Particularly in limbs, suggesting nerve involvement.
- Muscle Weakness: Due to nerve compression or joint damage.
Diagnostic Methods
- Physical Examination: Assessing joint function and pain levels.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, and CT scans to visualize structural changes.
- Blood Tests: Detecting markers of inflammation or autoimmune activity.
- Nerve Studies: Evaluating nerve function in spine disorders.
Treatment Options
Treating arthritis and spine disorders requires a multidisciplinary approach involving pain relief, mobility restoration, and long-term care.
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular Exercise: Strengthens joints and spine muscles
- Weight Management: Reduces load on joints
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Proper chairs, workspaces, and sleep posture
- Quit Smoking: Helps improve circulation and bone strength
- Mindfulness & Stress Relief: Reduces tension in muscles and inflammation
2. Medication Management
- Pain Relievers & NSAIDs: For symptomatic relief
- DMARDs & Biologics: For inflammatory types like RA or AS
- Steroids: For severe inflammation, but limited to short-term use
- Supplements: Calcium, Vitamin D, Glucosamine, Omega-3s
3. Physical Therapy
A licensed physiotherapist can help with:
- Posture correction
- Strength and flexibility training
- Pain relief through modalities like TENS or ultrasound
- Rehabilitation post-injury or surgery
4. Ayurvedic & Alternative Therapies
India’s traditional healing system, Ayurveda, offers a holistic approach:
- Abhyanga (oil massage)
- Panchakarma detox therapies
- Basti (medicated enema) for Vata balancing
- Herbal medicines like Shallaki, Guggulu, Rasna, Nirgundi
Other supportive therapies include:
- Acupuncture
- Chiropractic adjustments
- Yoga & meditation
5. Surgical Options (If Needed)
- Joint Replacements – For advanced hip or knee arthritis
- Spinal Surgery – Disc removal, spinal fusion, laminectomy
- Minimally Invasive Procedures – Lower recovery time, reduced risk
Surgery is typically a last resort, used only when conservative treatments fail.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
- Regular Exercise: Maintains joint flexibility and muscle strength.
- Healthy Diet: Anti-inflammatory foods can reduce symptoms.
- Posture Awareness: Proper alignment reduces spinal stress.
- Routine Check-Ups: Early detection and management of symptoms.
Conclusion
Arthritis and spine disorders demand more than just medication—they require a well-rounded, comprehensive approach. At Wada Paralysis & Sandhivat Center, we go beyond symptomatic relief to target the root causes of joint and spinal discomfort. Our treatment philosophy integrates expert medical care, personalized rehabilitation therapies, and holistic lifestyle modifications, ensuring long-term relief and functional recovery.
We understand that no two patients are the same. That’s why our experienced team of Ayurvedic specialists and physiotherapists craft customized care plans tailored to your specific condition, pain levels, mobility goals, and overall health status.
FAQs
Q1: What is the best treatment for arthritis-related back pain?
A combination of physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and lifestyle changes is often effective. In severe cases, surgical options may be considered.
Q2: Can spine disorders be cured without surgery?
Many spine disorders can be managed with non-surgical treatments like physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle adjustments. Surgery is typically a last resort.
Q3: How long does arthritis rehabilitation take?
Rehabilitation duration varies based on severity and individual response but generally spans several weeks to months. Consistency in therapy is key to improvement.
Q4: What lifestyle changes can reduce arthritis flare-ups?
Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular low-impact exercise, and following an anti-inflammatory diet can help minimize flare-ups.
Q5: Are spine disorders common with age?
Yes, degenerative spine conditions like osteoarthritis and disc degeneration are more prevalent with aging due to wear and tear on spinal structures.