Child Health Disorders: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
Children are susceptible to a variety of Children health disorders, ranging from acute infections to chronic conditions. Understanding these disorders, their causes, treatments, and preventive measures is crucial for ensuring the well-being of our young ones. This comprehensive guide delves into common child health disorders, offering insights into their management and prevention.

Common Child Health Disorders
1. Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections, including the common cold, flu, and bronchitis, are prevalent among children.
- Causes: Viruses such as rhinoviruses and influenza viruses.
- Symptoms: Coughing, sneezing, fever, and nasal congestion.
- Treatment: Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications.
- Prevention: Regular handwashing, vaccinations, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
2. Asthma
Asthma is a chronic condition and a common Child Health Disorders, characterized by inflammation of the airways that leads to breathing difficulties.
- Causes: Genetic factors, environmental allergens, and respiratory infections.
- Symptoms: Wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing.
- Treatment: Inhalers, corticosteroids, and avoiding triggers.
- Prevention: Identifying and minimizing exposure to allergens and irritants.
3. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
- Causes: Genetic factors, brain structure anomalies, and environmental influences.
- Symptoms: Inattention, impulsiveness, and hyperactivity.
- Treatment: Behavioral therapy, medications, and educational support.
- Prevention: Early diagnosis and intervention can mitigate symptoms.
4. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
ASD encompasses a range of developmental disorders affecting communication and behavior.
- Causes: Genetic mutations and environmental factors.
- Symptoms: Social challenges, repetitive behaviors, and communication difficulties.
- Treatment: Therapies focusing on behavior, speech, and occupational skills.
- Prevention: While not preventable, early intervention improves outcomes.
5. Obesity
Childhood obesity is a growing concern and a major Child Health Disorders, leading to various long-term health complications.
- Causes: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and genetic predisposition.
- Symptoms: Excess body weight, fatigue, and joint problems.
- Treatment: Nutritional counseling, increased physical activity, and behavioral therapy.
- Prevention: Encouraging healthy eating habits and regular exercise.
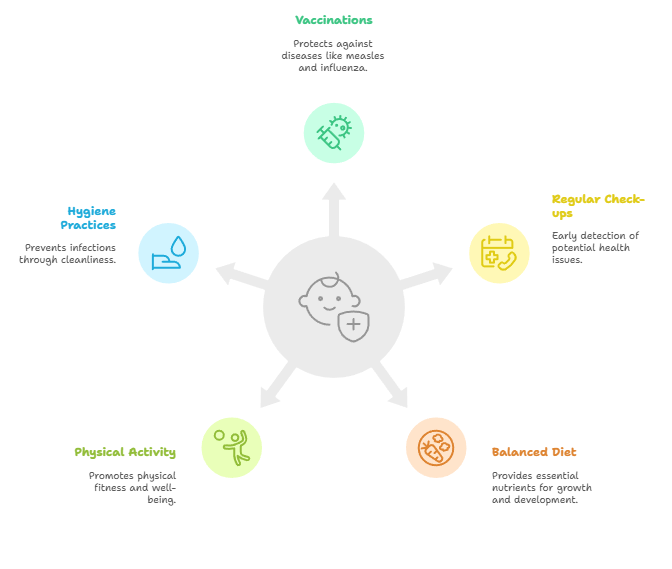
Preventive Measures
- Vaccinations: Ensure children receive recommended immunizations to protect against diseases like measles, mumps, and influenza.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine pediatric visits help in early detection and management of potential health issues.
- Balanced Diet: Provide a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Physical Activity: Encourage at least an hour of physical activity daily.
- Hygiene Practices: Teach proper handwashing and personal hygiene to prevent infections.
FAQs
Q1: How can I tell if my child has ADHD?
A: Signs include difficulty focusing, impulsive behavior, and hyperactivity. Consult a pediatrician for an accurate diagnosis.
Q2: What are early signs of autism in children?
A: Limited eye contact, delayed speech, and repetitive behaviors are common indicators. Early evaluation is essential.
Q3: How can I prevent my child from becoming obese?
A: Promote healthy eating, limit screen time, and encourage regular physical activity.
Q4: Are respiratory infections in children serious?
A: While often mild, some infections can lead to complications. Monitor symptoms and seek medical advice if concerned.
Q5: How often should my child have a health check-up?
A: Regular check-ups are recommended: annually for school-aged children and more frequently for younger ones.