Diabetes Care & Treatment: Comprehensive Guide for 2025
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. With the increasing prevalence of diabetes worldwide, understanding effective care and treatment options is crucial. This guide provides an in-depth look at the latest strategies for managing Diabetes Care , including lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and emerging technologies.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes Care involves managing elevated blood glucose levels caused by the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. There are several types of diabetes.
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, resulting from insulin resistance and often associated with lifestyle factors.
- Gestational Diabetes: Develops during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
- Prediabetes: A condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.

Latest Standards of Care
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) regularly updates its Standards of Care to reflect the latest research and clinical practices in Diabetes Care . The 2024 guidelines emphasize.
- Individualized Treatment Plans: Tailoring care based on patient preferences, comorbidities, and risk factors.
- Emphasis on Cardiovascular Health: Addressing blood pressure and cholesterol alongside glucose control.
- Use of Technology: Incorporating continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and digital health tools for better management.
- Mental Health Support: Recognizing the psychological impact of diabetes and providing appropriate resources.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are foundational in effective Diabetes Care , helping manage blood sugar levels and improve overall well-being naturally.:
- Nutrition: Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress Reduction: Practicing mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to manage stress levels.
Medical Treatments
Medications
Depending on the type and severity of diabetes, various medications may be prescribed as part of comprehensive Diabetes Care.
- Metformin: Often the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes.
- Insulin Therapy: Essential for type 1 diabetes and sometimes required for type 2.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Help lower blood sugar and promote weight loss.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: Assist in glucose excretion through urine and offer cardiovascular benefits.
Innovative Therapies
Recent advancements include:
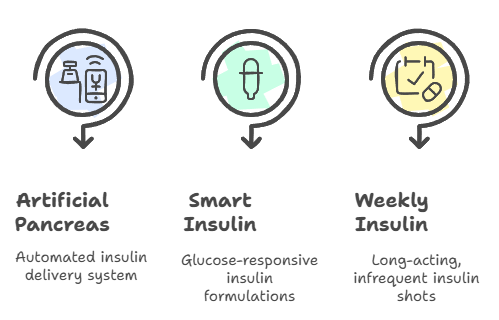
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: Devices that automate insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings.
- Smart Insulin: Insulin formulations that activate in response to blood sugar levels.
- Once-Weekly Insulin Injections: Long-acting insulins that reduce the frequency of injections
Monitoring and Technology
Regular monitoring is vital for effective diabetes management:
- Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): Using glucometers to check blood sugar levels.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Provides real-time data and trends.
- Mobile Apps: Track diet, exercise, and glucose levels for better self-management.
Preventing Complications
Proper diabetes management reduces the risk of complications:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Neuropathy: Monitoring for nerve damage symptoms and maintaining foot care.
- Retinopathy: Regular eye exams to detect vision issues early.
- Kidney Disease: Monitoring kidney function through regular tests.
FAQs
- Q1: Can diabetes be cured?
A: Currently, there’s no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes and medical treatments. - Q2: Is insulin therapy only for type 1 diabetes?
A: While essential for type 1, insulin may also be prescribed for type 2 diabetes when other treatments are insufficient. - Q3: How often should I check my blood sugar?
A: Frequency depends on your treatment plan; consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice. - Q4: Are there any new treatments for diabetes?
A: Yes, innovations like artificial pancreas systems and smart insulin are emerging to improve management. - Q5: Can lifestyle changes alone manage diabetes?
A: In early stages or prediabetes, lifestyle modifications can be highly effective; however, some individuals may require medications.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and regular monitoring. Diabetes Care involves staying informed about the latest advancements and working closely with healthcare professionals, which can lead to better outcomes and an improved quality of life.