Skin Disorders: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
Skin is the body’s largest organ and a key player in our health and self-image. But when something goes wrong, it shows — through irritation, rashes, discoloration, bumps, and chronic conditions. Skin disorders affect millions globally, from mild acne to serious autoimmune diseases. This comprehensive guide will help you understand common skin disorders, their causes, effective treatments, and best practices for prevention and care.
What Are Skin Disorders?
Skin disorders are medical conditions that affect the skin’s appearance, texture, or function. These issues may be temporary or chronic, localized or widespread. Some are genetic, others are environmental, and many are a mix of both.
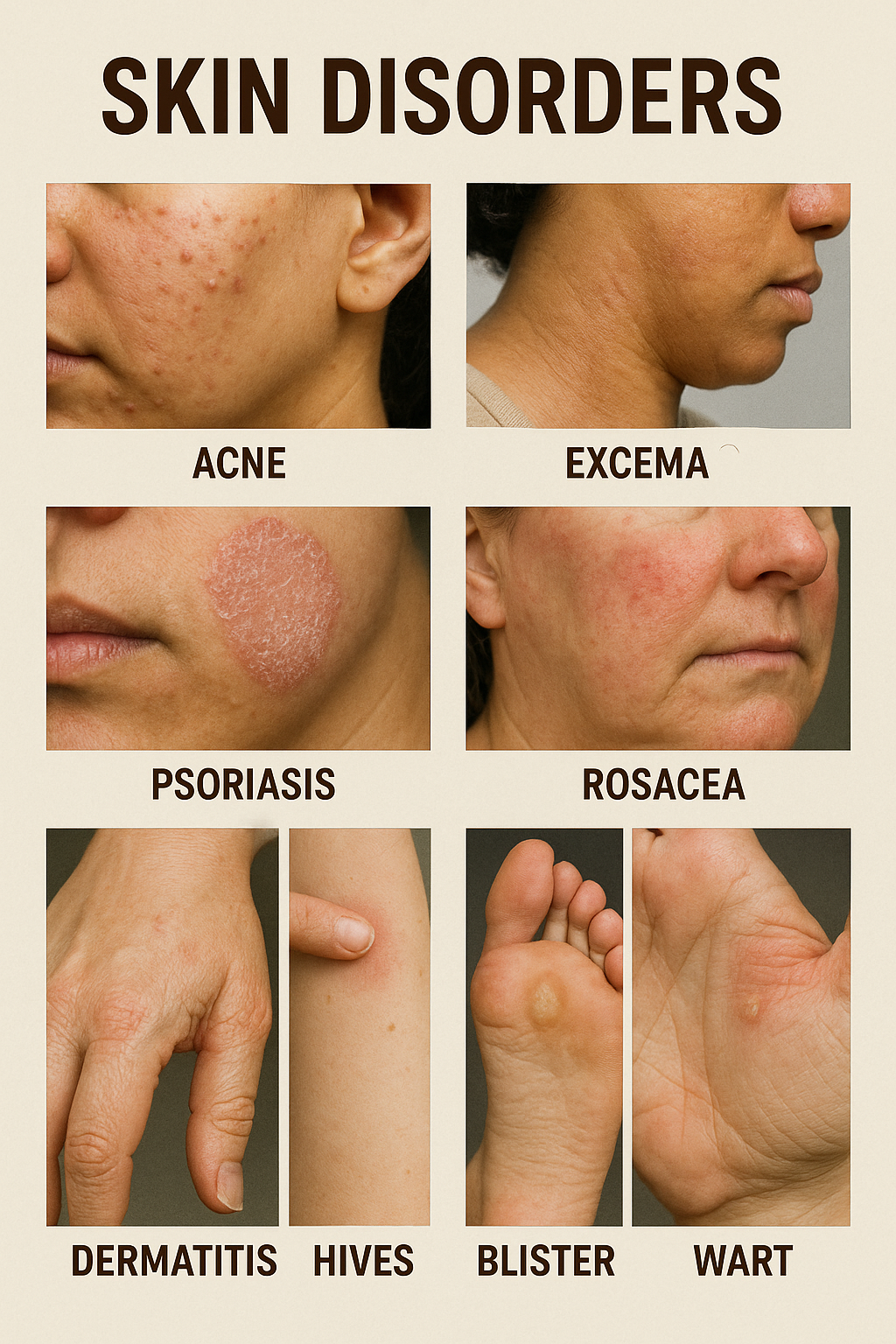
Common Types of Skin Disorders
1. Acne
- Cause: Clogged pores from oil, bacteria, dead skin cells.
- Symptoms: Pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts.
- Treatments: Topical creams, oral medications, laser therapy, diet modifications.
2. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Cause: Immune system overreaction, genetic predisposition.
- Symptoms: Dry, itchy, inflamed patches, often on hands and knees.
- Treatments: Moisturizers, antihistamines, corticosteroid creams.
3. Psoriasis
- Cause: Autoimmune disease speeding up skin cell growth.
- Symptoms: Red, scaly patches, often on elbows, knees, and scalp.
- Treatments: Topicals, light therapy, biologic medications.
4. Rosacea
- Cause: Unclear, but includes immune response, genetics, and environmental triggers.
- Symptoms: Redness, visible veins, acne-like bumps, eye irritation.
- Treatments: Anti-inflammatory medication, laser treatment, skincare modifications.
5. Fungal Infections (Ringworm, Athlete’s Foot)
- Cause: Fungi in warm, moist environments.
- Symptoms: Itchy, red, ring-shaped rash or flaking.
- Treatments: Antifungal creams, powders, oral meds.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Persistent itchiness or dryness
- Changes in mole size, color, or shape
- Redness, scaling, or flaking
- Unexplained rashes or blisters
- Sudden sensitivity or pigmentation
Early intervention is key. If your symptoms persist for more than a week or worsen, consult a dermatologist immediately.
Skin Disorder Causes and Risk Factors
- Genetics: Many conditions like psoriasis and eczema run in families.
- Allergens & Irritants: Fragrances, detergents, and harsh soaps can cause reactions.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Particularly common in acne and melasma.
- Diet & Nutrition: Deficiencies in vitamins A, D, E, and zinc affect skin health.
- Environment: Pollution, sun exposure, and climate can trigger flare-ups.
- Stress: Can worsen eczema, psoriasis, and acne.
Effective Treatments for Skin Disorders
1. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
- Acne creams with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide.
- Antihistamines for allergic reactions.
- Antifungal ointments for ringworm and athlete’s foot.
2. Prescription Medications
- Corticosteroids for inflammation.
- Antibiotics for infected or severe acne.
- Retinoids for cell turnover.
- Biologics for autoimmune conditions like psoriasis.
3. Non-Medication Therapies
- Phototherapy for psoriasis and eczema.
- Laser treatments for rosacea and pigmentation.
- Chemical peels and facials for acne-prone skin.
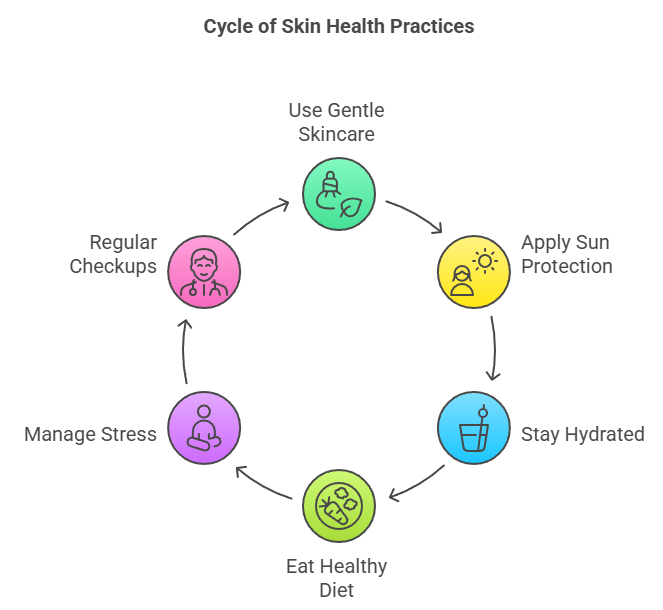
How to Prevent Skin Disorders
- Use Gentle Skincare: Avoid products with alcohol, synthetic fragrance, and sulfates.
- Sun Protection: Use SPF 30+ sunscreen daily.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep skin moist and supple.
- Healthy Diet: Include foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3s.
- Manage Stress: Meditation, exercise, and proper sleep.
- Regular Checkups: Visit a dermatologist annually or as needed.
FAQs About Skin Disorders
Q1: What is the most common skin disorder?
A: Acne is the most common, affecting around 85% of people between the ages of 12 and 24.
Q2: Are all skin disorders treatable?
A: While some are chronic, most skin disorders can be effectively managed with the right treatment plan.
Q3: Can stress really affect skin conditions?
A: Yes, stress is a proven trigger for conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
Q4: When should I see a dermatologist?
A: If over-the-counter products aren’t working, or if you notice a sudden or worsening skin issue.
Q5: Can diet improve skin disorders?
A: Absolutely. A diet rich in leafy greens, healthy fats, and vitamin-rich foods supports better skin health.
Conclusion
Skin disorders are common but manageable with the right knowledge and care. Whether you’re dealing with occasional breakouts or chronic conditions, proper skin hygiene, early diagnosis, and personalized treatments can make all the difference. Always consult with a qualified dermatologist to develop a skincare strategy tailored to your specific needs.